In this tutorial, we will discuss how to transfer files among systems using SCP & Rsync with some examples. We will also discuss SCP & RSYNC command line options to make use of the commands to the fullest.
Also Read: Cloning disks using dd & cat commands
SCP & Rsync commands
SCP is based on ssh & is used to transfer files from localhost to remote host securely.
The syntax for using SCP is
# scp source_file_name username@destination_host:destination_folder
Rsync’s main function, on the other hand, is basically to synchronize files/directories either on localhost or on the remote host. Rsync initially copies the whole directory & then copies the newly added files (differential backup) rather than copying the whole directory again.
It is secure & faster than SCP & can also be used in place of the SCP command to copy files/directories to the remote hosts.
The syntax for using rsync is
# rsync options source destination
Now, let us discuss some examples showing the uses of both commands.
Examples for SCP command line options
# scp –rpv /datafile dan@192.168.1.100:/home/susan
here, option r is used when we are copying a directory with all the files inside it,
secondly, option p will provide an estimated time & connection speed,
and option v will provide debugging information that can help in diagnosing a problem related to connection, authentication, etc.
# scp –C /datafile dan@192.168.1.100:/home/susan
option C here will compress the file on the go & will reproduce the same file when it arrives at the destination. Thus saving time consumed for copying the file.
# scp -P 300 /datafile dan@192.168.1.100:/home/susan
here option –P is used to define a custom port in case we are not using the default ssh port (22).
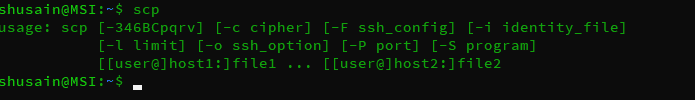
Get complete list of options that can be used with SCP by running,
Examples for Rsync command line options
# rsync -azvh /datafile dan@192.168.1.100:/home/susan
here, option r is archive mode which allows copying of files recursively along with their file permissions, symbolic links, etc,
The second option r is used to compress file data,
third option h will provide human-readable outputs,
and option v will provide debugging information that can help in diagnosing a problem related to connection, authentication, etc,
Also, we can mention a local location like /home/dan in place of dan@192.168.1.100:/home/susan
# rsync -azvh --progress dan@192.168.1.100:/home/susan /datafile
The above example will let us synchronize a directory from a remote location to the localhost directory & --progress will show us the progress of file/directory transfer.
# rsync –avzhe ssh /datafile dan@192.168.1.100:/home/susan
this example will let us use rsync over ssh and option –e here is used to define a protocol, which in this case is ssh.
# rsync –avzhe ‘ssh –p 300’ /datafile dan@192.168.1.100:/home/susan
here, this example will let us use rsync over ssh with the modified port.
# rsync -azvh --progress --include 'A*' --exclude '*' dan@192.168.1.100:/home/susan /datafile
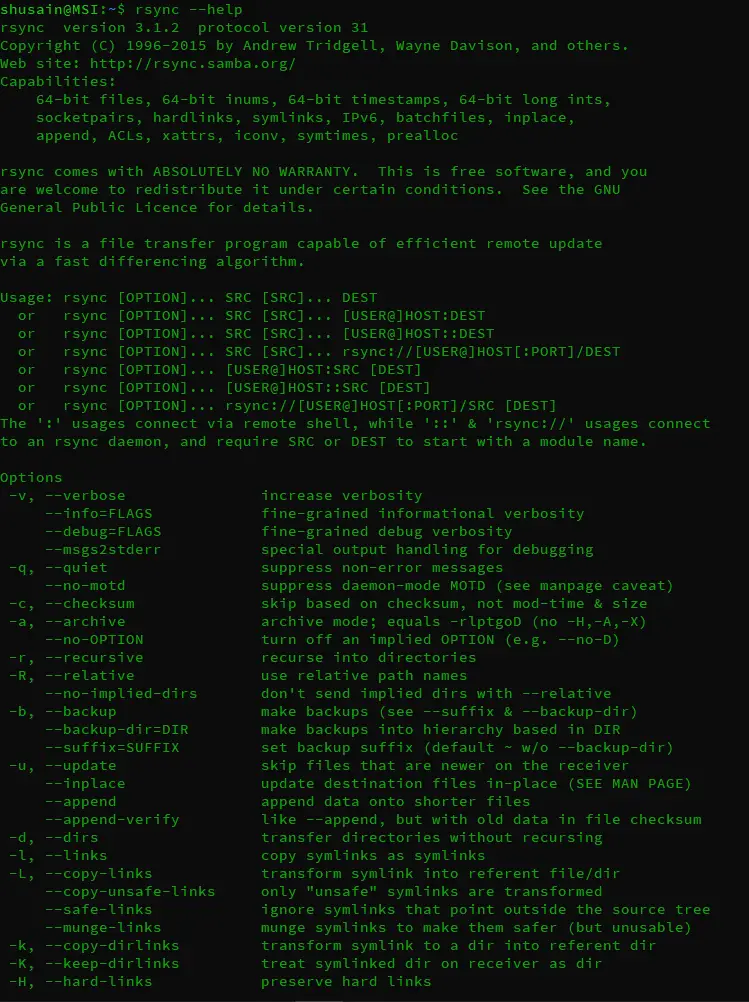
this will let us copy all files starting with "A" & will exclude all other files. Get the complete list of options that can be used with rsync by running the following command,
Both the scp & rsync can be used to transfer files/directories but rsync fares a little better when comes to performance. Also, Rsync command line options allow us to take differential backup which scp can not do. But both are equally secure & very easy to use.
This was our tutorial on how to use SCP & Rsync command line options in Linux. Please do let us know if you have any questions or queries using the comment box below.
This is very good but it does not work with AWS servers. Still missing public keys. How to identify the public key on the sending and receiving servers.
For AWS, you should have ports opened in your security group & also you can enable password-less ssh login.
small typo in the article when describing the options avzh
currently says
“here, option r” should be “here, option a”
“Second option r” should be “Second option z”
==
rsync –azvh /datafile dan@192.168.1.100:/home/susan
here, option r is archive mode which allows copying of files recursively along with their file permissions, symbolic links etc,
Second option r is used to compress file data,
third option h will provide human readable outputs,
and option v will provide debugging information which can help in diagnosing a problem related to connection, authentication etc,
Hi,
Is there an option to use rsync command with http URL?
I want to sync my local repo with remote maven repo.
I have tried rsync -avhz http://example.com/mr/ds /home/.m2/repository
but it didn’t work for me.
Could you please help me on this?
With rsync, its not possible but there is another command you can use called zsync. Though i have not used it personally but i am aware that this will help you out.
Hi Shusain,
Thank you for the suggestion.
Zsync will do partial/differential file download.
We have to mention the file name which we want to download in every time.
Ex: zsync http://example.com/some/filename.zsync
In my case I want incremental download of complete repository.
Please correct me if I am wrong.