One of the major work of a System Administrator is User & Group Management. We have to create new users & groups, delete old ones, providing users access to a group or folder etc etc. So, in this tutorial, we will learn how we can manage users & groups.
Linux systems have two types of users, general/normal user and root/super user . While general users have limited access to the Linux system, root users have access to anything & everything on the Linux system.
When a user is created a group with the same user name is also created. Every user has its own home directory, for user root its /root & for general users its located in /home/. Records with all the user information for all the users is maintained in /etc/passwd file & records for all the groups are kept /etc/group.
Let’s discuss these files in brief before we discuss the commands for user & group management
(Recommended Read: Learn how to use tcpdump command with examples)
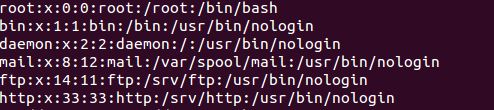
/etc/passwd
This file contains list of all users with every line of the file containing information regarding single user. Format for each line is
Username:x:UID:GID:Comment:Home Directory: Default shell
Here, x is password for the user in encrypted form (stored in /etc/shadow file)
UID, is the user id
& GID is the group id for the user.
/etc/group
Just like /etc/passwd, it contains information for groups with each line having information for single group. Format for entries in this file is
Group name:x:GID:members

Where, x again means password in encrypted format.
Now let’s discuss commands for user & group management.
USER Management
Below mentioned are the commands that are used for user management,
Purpose Command
- Adding a user useradd dan
- Assigning password to user passwd dan
- Changing home directory for user useradd dan –d /home/new
- Setting expiry for user useradd dan –e 2017-11-25
- Addding inactive period before expiry useradd dan –f 2
- Changing default shell useradd dan –s /bin/sh
- Removing user userdel dan
- Removing user with home directory userdel –r dan
We can also modify default settings of a user after it has bee added with usermod command
- Setting expiry for user usermod –e 2017-11-25 dan
- Changing home directory usermod –d /home/new dan
- Changing default shell usermod –s /bin/sh dan
- Locking an account usermod –L dan
- Unlocking a locked account usermod –u dan
Group Management
Following are the commands for managing groups
- Adding a group groupadd linuxgroup
- Adding user to group usermod –aG linuxgroup dan
- Changing owner & group of a file chown dan:linuxgroup newfile.txt
- Changing only owner of a file chown dan: newfile.txt
- Changing only group of a file chown :linuxgroup newfile.txt
- Deleting a group groupdel linuxgroup
This completes our tutorial on user & group management. We will also discuss File permissions & permission management in our future tutorial.
Don’t forget to mention your queries/comments in the comment box down below.
If you think we have helped you or just want to support us, please consider these :-
Connect to us: Facebook | Twitter | Google Plus
Donate us some of you hard earned money: [paypal-donation]
Linux TechLab is thankful for your continued support.
