If you are a Linux system administrator or just a Linux enthusiast/lover, then you love & use command line aks CLI. Until some years ago the majority of Linux work was accomplished using CLI only & even there are some limitations to GUI. Though there are plenty of Linux distributions that can complete tasks with GUI but still learning CLI is a major part of mastering Linux. To this effect, we present you with a list of useful Linux commands that you should know.
Recommended Read : Top 7 commands for Linux Network Traffic Monitoring
Also Read: Complete “Beginners to PRO” guide for GIT commands
Note:- There is no definite order to all these commands & all of these commands are equally important to learn & master in order to excel in Linux administration. One more thing, we have only used some of the options for each command, for example, you can refer to 'man pages' for a complete list of options for each command.
1- top command
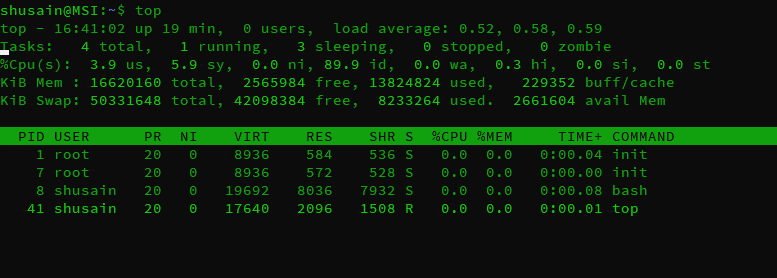
The 'top' command displays the real-time summary/information of our system. It also displays the processes and all the threads that are running & are being managed by the system kernel.
Information provided by the 'top' command includes uptime, the number of users, Load average, running/sleeping/zombie processes, CPU usage in percentage based on users/system, etc, system memory free & used, swap memory, etc.
To use top command, open terminal & execute the command,
$ top
To exit out the command, either press 'q' or 'ctrl+c'.
2- free command
The 'free' command is used to specifically used to get the information about system memory or RAM. With this command, we can get information regarding physical memory, swap memory as well as system buffers. It provided the amount of total, free & used memory available on the system.
To use this utility, execute the following command in terminal
$ free
It will present all the data in kb or kilobytes, for megabytes use options '-m' & '-g ' for GB.
3- cp command
'cp' or copy command is used to copy files among the folders. The syntax for using the 'cp' command is,
$ cp source destination
4- cd command
'cd' command is used for changing the directory. We can switch among directories using the 'cd command.
To use it, execute
$ cd directory_location
5- ifconfig
'Ifconfig' is a very important utility for viewing & configuring network information on a Linux machine.
To use it, execute
$ ifconfig
This will present the network information of all the networking devices on the system. There are a number of options that can be used with 'ifconfig' for configuration, in fact, they are many options that we have created a separate article for it (Read it here || IFCONFIG command : Learn with some examples ).
6- crontab command
'Crontab' is another important utility that is used to schedule a job on a Linux system. With crontab, we can make sure that a command or a script is executed at the pre-defined time. To create a cron job, run
$ crontab -e
To display all the created jobs, run
$ crontab -l
You can read our detailed article regarding crontab ( Read it here || Scheduling Important Jobs with Crontab )
7- cat command
'cat' command has many uses, most common use is that it's used to display the content of a file,
$ cat file.txt
But it can also be used to merge two or more file using the syntax below,
$ cat file1 file2 file3 file4 > file_new
We can also use the 'cat' command to clone a whole disk (Read it here || Cloning Disks using dd & cat commands for Linux systems)
8- df command
'df' command is used to show the disk utilization of our whole Linux file system. Simply run.
$ df
& we will be presented with disk complete utilization of all the partitions on our Linux machine.
9- du command
'du' command shows the amount of disk that is being utilized by the files & directories on our Linux machine. To run it, type
$ du /directory
(Recommended Read: Use of du & df commands with examples)
10- mv command
'mv' command is used to move the files or folders from one location to another. Command syntax for moving the files/folders is,
$ mv /source/filename /destination
We can also use the 'mv' command to rename a file/folder. Syntax for changing name is,
$ mv file_oldname file_newname
11- rm command
'rm' command is used to remove files\folders from the Linux system. To use it, run
$ rm filename
We can also use the '-rf' option with the 'rm' command to completely remove a file\folder from the system but we must use this with caution.
12- vi/vim command
VI or VIM is very famous & one of the widely used CLI-based text editors for Linux. It takes some time to master it but it has a great number of utilities, which makes it a favorite for Linux users.
For detailed knowledge of VIM, kindly refer to the articles Beginner’s Guide to LVM (Logical Volume Management) & Working with Vi/Vim Editor : Advanced concepts.
13- ssh command
SSH utility is to remotely access another machine from the current Linux machine. To access a machine, execute
$ ssh username@IPaddress OR machine_name
Once we have remote access to the machine, we can work on the CLI of that machine as if we are working on the local machine.
14- tar command
'tar' command is used to compress & extract the files\folders. To compress the files\folders using tar, execute
$ tar -cvf file.tar file_name
where file.tar will be the name of compressed folder & 'file_name' is the name of source file or folders. To extract a compressed folder,
$ tar -xvf file.tar
For more details on the 'tar' command, read Tar command : Compress & Decompress the files\directories
15- locate command
'locate' command is used to locate files & folders on your Linux machines. To use it, run
$ locate file_name
16- grep command
'grep' command another very important command that a Linux administrator should know. It comes especially handy when we want to grab a keyword or multiple keywords from a file. Syntax for using it is,
$ grep 'pattern' file.txt
It will search for 'pattern' in the file 'file.txt' and produce the output on the screen. We can also redirect the output to another file,
$ grep 'pattern' file.txt > newfile.txt
17- ps command
'ps' command is especially used to get the process id of a running process. To get information of all the processes, run
$ ps -ef
To get information regarding a single process, executed
$ ps -ef | grep java
18- kill command
The 'kill' command is used to kill a running process. To kill a process we will need its process id, which we can get using the above 'ps' command. To kill a process, run
$ kill -9 process_id
19- ls command
'ls' command is used to list all the files in a directory. To use it, execute
$ ls
20- mkdir command
To create a directory in a Linux machine, we use the command 'mkdir'. Syntax for using 'mkdir' is
$ mkdir new_dir
These were some of the most useful Linux commands that every System Admin should know, we will soon be sharing another list of some more important commands that you should know being a Linux lover. You can also leave your suggestions and queries in the comment box below.

It’s less a command and more a utility but midnight commander (mc), is one helluva tool worth knowing. It brings a pseudo-graphical and familiar interface (twin pane file manager) to the command line. It brings together many of the functions of these tools you’ve listed plus more. Want to peak into the contents of a zip/tar/tgz/deb file without opening it? Done. Want to visually mark files to be deleted or moved into the opposite directory. Done. (With file counts, total bytes, and file globbing for file selection). Done. Want to remotely mount another file system as one of the directory panes using sft or smb (with compilation tweaks). Done.
I agree with needing to know all of these with one exception … number 5, ifconfig. In most of the distributions currently ifconfig has been deprecated in favor of the ip command. So, not that knowing ifconfig is a bad thing, but .. for someone that needs to know these commands and is just starting to “get their feet wet” with Linux administration, they’d be better off knowing the “ip” command instead and if necessary, learning about ifconfig usage later….just an observation. I’m not trying to step on anyone’s toes here.