System Admins are required to monitor IT infrastructure to make sure that everything is up & running. We have to monitor performance of hardware i.e memory, hdds & CPUs etc & so does we have to monitor our network. We need to make sure that our network is not being over utilised or our applications, websites might not work. In this tutorial, we are going to learn to use IFTOP utility.
(Recommended read : Resource monitoring using Nagios, Tools for checking system info, Important logs to monitor)
Iftop is network monitoring utility that provides real time monitoring network bandwidth. Iftop measures total data moving in & out of the individual socket connections i.e. it captures packets moving in and out via network adapter & than sums those up to find the bandwidth being utilised.
Installation on Debian/Ubuntu
Iftop is available with default repositories of Debian/Ubuntu & can be simply installed using the command below,
$ sudo apt-get install iftop
Installation on RHEL/Centos using yum
For installing iftop on CentOS or RHEL, we need to enable EPEL repository. To enable repository, run the following on your terminal,
RHEL/CentOS 8
$ sudo dnf install https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-8.noarch.rpm
RHEL/CentOS 7
$ rpm -Uvh https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/7/x86_64/Packages/e/epel-release-7-11.noarch.rpm
RHEL/CentOS 6 (64 Bit)
$ rpm -Uvh http://download.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/6/x86_64/epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm
RHEL/CentOS 6 (32 Bit)
$ rpm -Uvh http://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/6/i386/epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm
After epel repository has been installed, we can now install iftop by running,
$ yum install iftop
This will install iftop utility on your system. We will now use it to monitor our network,
Using IFTOP
You can start using iftop by opening your terminal windown & type,
$ iftop
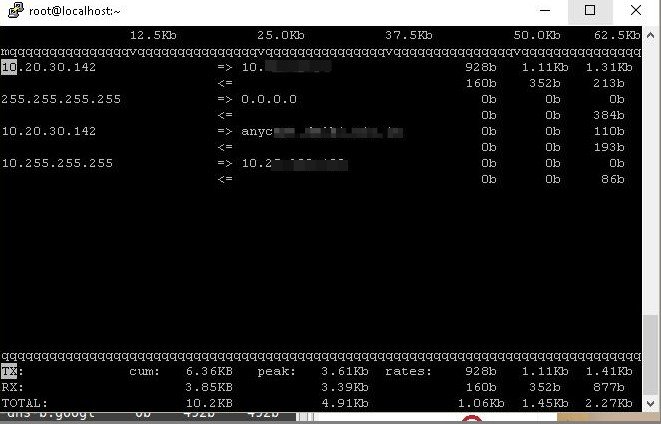
You will now be presented with network activity happening on your machine. You can also use
$ iftop –n
Which will present the network information on your screen but with ‘-n’ , you will not be presented with the names related to IP addresses but only ip addresses. This option allows for some bandwidth to be saved, which goes into resolving IP addresses to names.
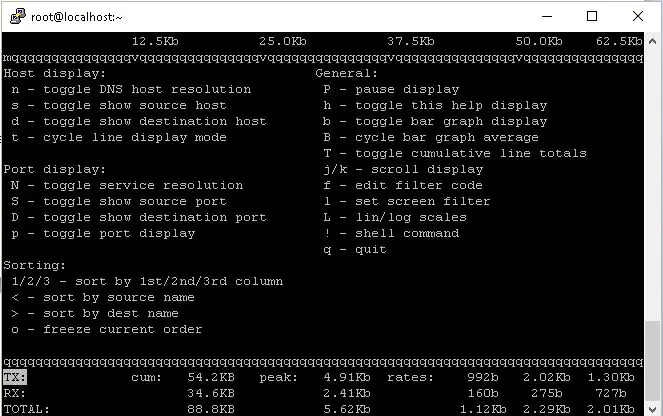
Now we can also see all the commands that can be used with iftop. Once you have ran iftop, press ‘h’ button on the keyboard to see all the commands that can be used with iftop.
To monitor a particular network interface, we can mention interface with iftop,
$ iftop –I enp0s3
You can check further options that are used with iftop using help, as mentioned above. But these mentioned examples are only what you might to monitor network. We now end this tutorial on Monitoring network bandwidth using Iftop command. Please do send us your questions or queries using the comment box below.
If you have found this article to be useful, please share it among your friends/colleagues/followers. THANKS !!!
If you think we have helped you or just want to support us, please consider these :-
Connect to us: Facebook | Twitter | Google Plus
Become a Supporter - Donate us some of you hard earned money: [paypal-donation]
Linux TechLab is thankful for your continued support.
